Lean Visual Management: Essential Tools and Implementation Strategies

| Audience: | Manufacturing Managers, Healthcare Administrators, Operational Excellence and Lean Management Practitioners, HR Coordinators, Organizational Leaders |
| Last updated: | November 10, 2025 |
| Read time: | 4 min |
- Visual clarity improves efficiency: Tools like Kanban, Andon, and 5S make workflows visible, reducing delays and errors.
- Supports lean principles: LVM reinforces pull systems, standardization, and problem-solving across teams.
- Drives agility and engagement: By involving frontline workers and tracking KPIs visually, organizations foster a culture of accountability and adaptability.
Lean management continues to shape the future of manufacturing by focusing on eliminating waste, reducing cycle times, and enhancing both customer and employee experiences. At the core of this methodology lies visual management—a critical practice for driving operational excellence on the shop floor and beyond.
What Is Lean Visual Management?
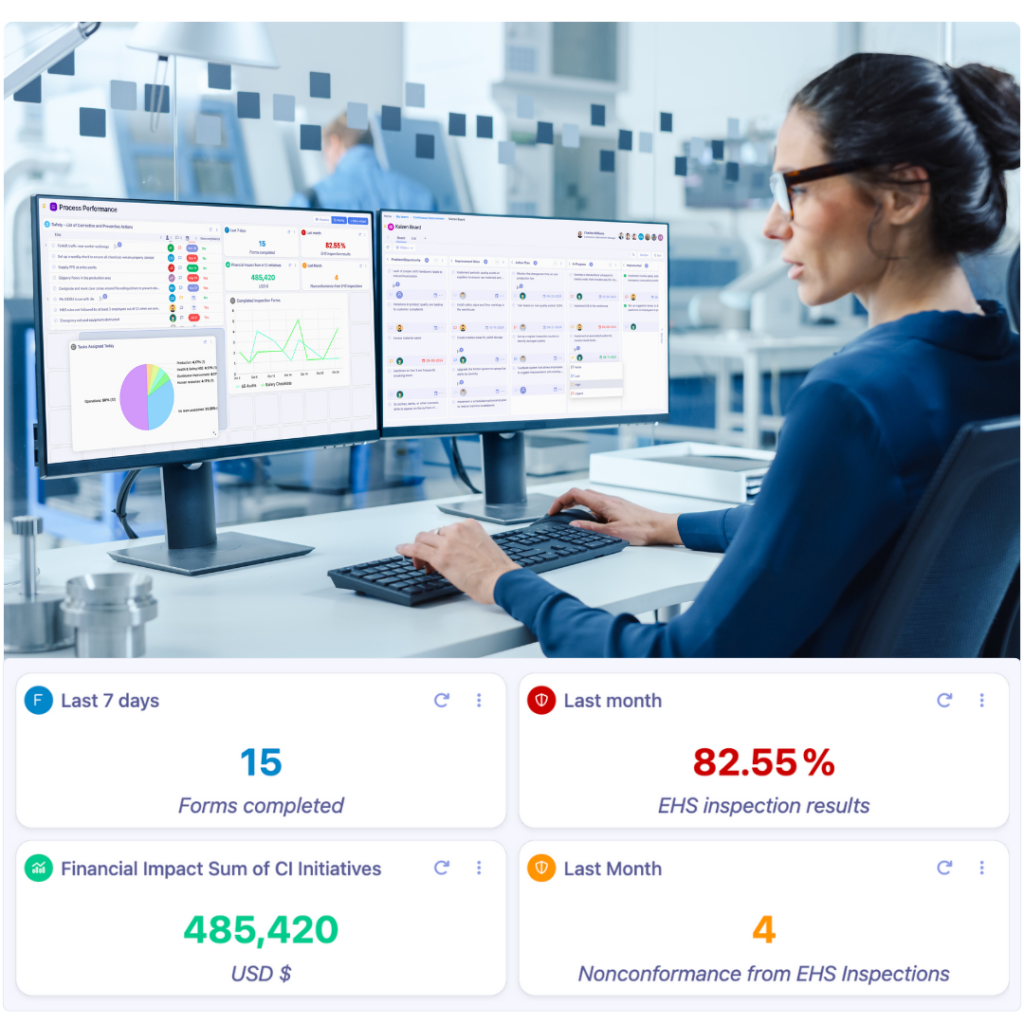
Lean Visual Management (LVM) uses visual tools and systems to make information visible, understandable, and actionable in real time. In dynamic environments like shop floors, hospitals, and logistics centers, people respond faster to visual signals than to written instructions. By tapping into this visual instinct, organizations can streamline communication, accelerate decision-making, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Visual tools such as floor markings, status boards, and digital dashboards make workflows transparent and standardized. This transparency reinforces safety practices, reduces ambiguity, and ensures everyone—from frontline workers to senior leaders—operates from the same playbook.
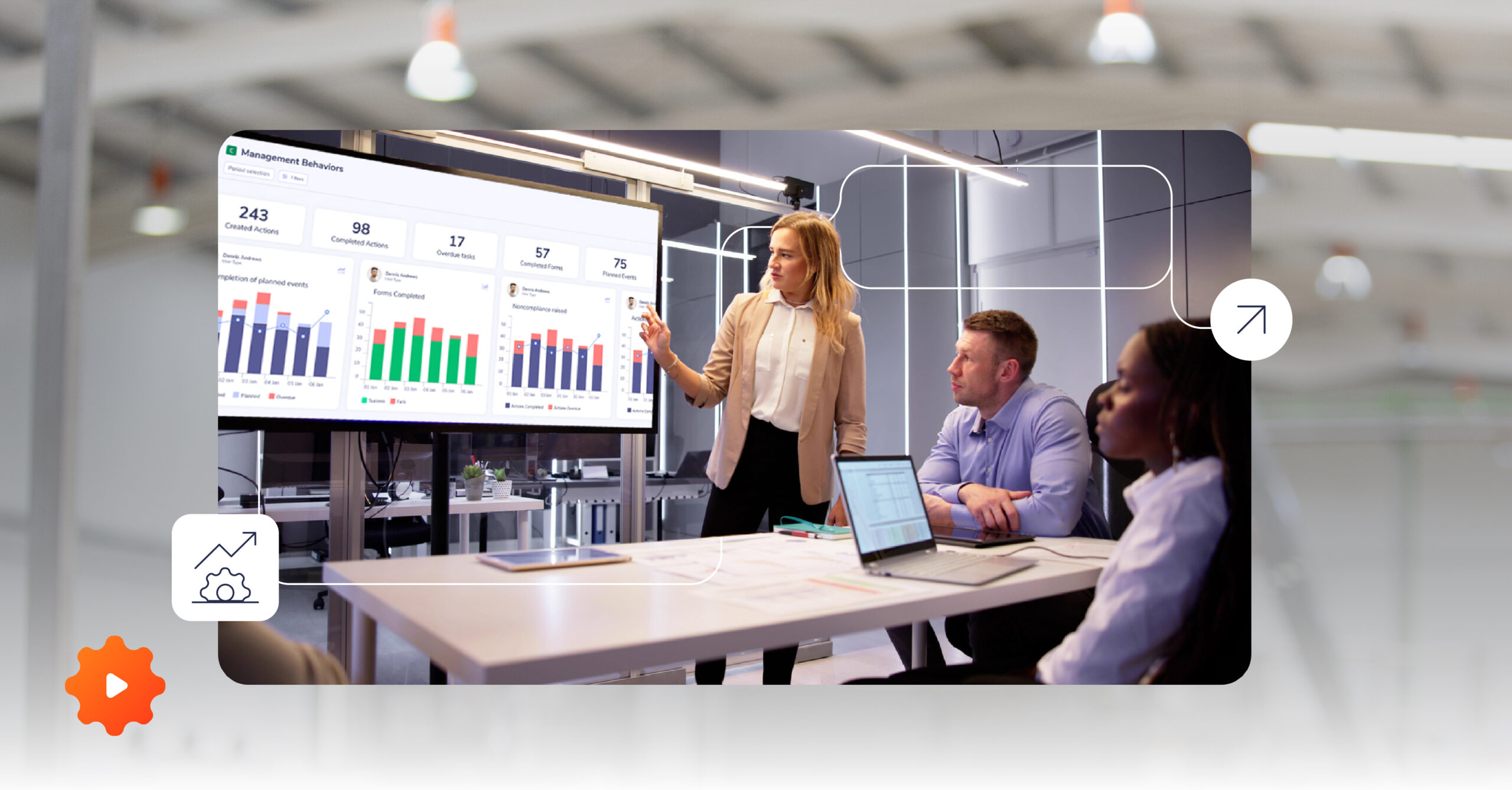
Core Principles of Lean Visual Management
To implement LVM effectively, manufacturers and healthcare organizations should align with five foundational lean principles:
- Identify Value
Define customer needs clearly to ensure every process step adds measurable value. - Map the Value Stream
Visualize workflows and resource allocations to detect delays, redundancies, and bottlenecks. - Create Flow
Break down complex processes into visual sequences that enable smooth transitions and clear accountability. - Establish Pull Systems
Use visual cues to limit WIP (Work in Progress), enabling just-in-time delivery and minimizing waste. - Pursue Continuous Improvement
Make ongoing reviews part of daily operations. Visual tools like Kaizen boards and PDCA cycles help teams track improvements and address recurring issues.

Key Benefits of Lean Visual Management
LVM is more than aesthetics—it’s a strategic enabler for performance. When implemented correctly, it delivers tangible benefits across operations:
- Faster problem detection: Visual cues and real-time data alerts flag issues before they escalate.
- Waste reduction: Identifies non-value-added activities and supports sustainability goals.
- Lower operational costs: Minimizes rework, overproduction, and inefficient resource use.
- Shorter lead times: Visual workflows reduce delays and enhance responsiveness.
- Optimized inventory: Better visibility prevents understocking or overstocking.
- Improved safety: Standardized visuals reinforce compliance with safety procedures.
Tools That Support Visual Management
Several tried-and-tested tools support lean visual management:
- Kanban Boards
Use color-coded cards to signal work progress and control workflow. Ideal for managing production stages or patient flow in clinical settings.
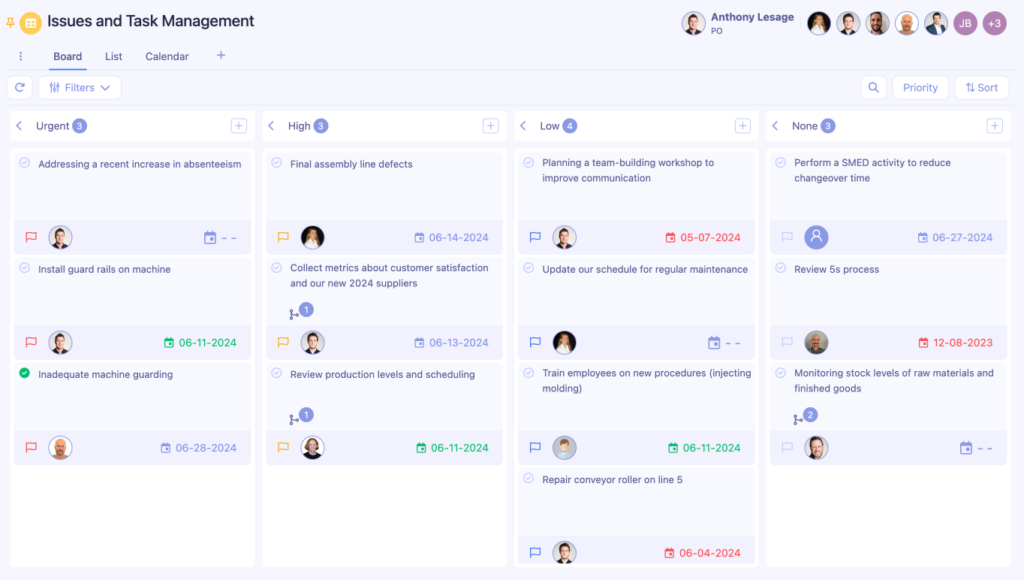
- Andon Systems
Signal lights and alert displays enhance quality control and notify teams of process disruptions in real time. These tools enable immediate intervention, crucial in high-stakes manufacturing and healthcare environments. - 5S Visuals
Based on the Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain method. 5S labels, floor markings, and visual storage maps ensure workplace organization and efficiency. - Gemba Boards
Used on the production floor to display KPIs related to safety, quality, delivery, and cost. Employees update them regularly to foster accountability and improve performance tracking.

10 Visual Management Must-Haves [eBook]
Implementing Lean Visual Management: Step-by-Step
A structured rollout ensures long-term success. Here’s a typical implementation roadmap:
- Assess the Current State
Analyze current processes to pinpoint inefficiencies and prioritize improvement areas. - Define the Vision
Align your LVM strategy with broader organizational goals—be it reducing errors in patient care or boosting first-pass yield in manufacturing. - Design the System
Select relevant tools and design visuals that clearly convey the right information at the right time. - Deploy and Train
Introduce the system gradually and train teams thoroughly to ensure proper usage and buy-in. - Monitor and Adjust
Conduct regular reviews, audits, and feedback loops to fine-tune the system and sustain momentum.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Rolling out visual management comes with hurdles. Here’s how to tackle them:
- Resistance to Change: Involve frontline teams early. Their input strengthens adoption and system relevance.
- Resource Constraints: Focus on high-impact areas first. Simple visuals often deliver significant returns.
- Process Complexity: Break down steps and standardize visual language to ease understanding.
- Sustainability: Embed visual reviews into daily huddles and leader standard work to keep improvements alive.
- Scalability: Choose tools that can evolve with your operations, whether across multiple shifts or sites.
Creating a Visual Workplace
A visual workplace integrates cues, markings, dashboards, and standards across the facility. Whether it’s a patient room, maintenance bay, or assembly line, every worker should understand expectations and performance metrics at a glance. Visual management also aids onboarding and continuous training, making knowledge transfer more efficient.
Best Practices for Visual Management Success
- Design for clarity: Avoid clutter. Use color coding and consistent symbols.
- Keep visuals current: Outdated boards erode trust and usefulness.
- Train continuously: Make visual management part of operational discipline.
- Audit regularly: Use checklists and walkthroughs to verify compliance and effectiveness.
- Encourage feedback: Let users refine and improve the system.
Next Steps: Driving Sustained Improvement
Lean Visual Management is not a one-time project—it’s an evolving system. The key is consistent application, leadership support, and ongoing iteration. When properly deployed, LVM enhances agility, reduces friction, and equips teams to respond faster to challenges and opportunities.
Tervene’s visual management tools help manufacturers and healthcare leaders implement effective visual management systems that connect frontline teams with real-time data.
Book a demo to discover how visual tools can transform your operational performance.
Gain visibility with Tervene’s visual management system
Explore Tervene’s visual management toolsLean Visual Management – FAQ
Lean Visual Management (LVM) is the use of visual tools—such as boards, indicators, and labels—to make work processes, performance, and issues immediately visible. It supports Lean goals like waste reduction, standardization, and continuous improvement.
In fast-paced environments like shop floors, visual cues accelerate understanding and decision-making. They help teams detect issues early, follow standardized procedures, and align around shared goals—all critical for improving productivity and safety.
LVM highlights inefficiencies by making workflows transparent. Visual tools expose bottlenecks, excess inventory, or quality issues, enabling faster corrective actions and minimizing non-value-added activities.
Common tools include:
-
Kanban boards for workflow control
-
Andon systems for issue escalation
-
5S visuals for organization and cleanliness
-
Gemba boards for tracking operational KPIs
Yes. Digital platforms integrate real-time data with visual dashboards, enabling better tracking, collaboration, and responsiveness across multiple teams and locations.
Start by assessing current workflows, then define a visual strategy aligned with business goals. Select appropriate tools, train teams, and monitor performance regularly to drive sustained improvement.
While manufacturing leads adoption, healthcare, logistics, and other complex, high-compliance sectors increasingly rely on visual management to improve safety, quality, and efficiency.

























